This month's newsletter focuses on Research Theme 2 - Support the Engineer.
IN THE SPOTLIGHT #
Congratulations to Braden Thorne on his paper "Reservoir time series analysis: Using the response of complex dynamical systems as a universal indicator of change", which was selected as an Editor's Pick in the journal Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science.
HIGHLIGHTS #
The Centre was very pleased to host Prof Geert-Jan van Houtum, Chair of Maintenance and Reliability at Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands. Prof van Houtum facilitated workshops with our PhD students at both Curtin and UWA. He shared his valuable experience and knowledge on their topics. We hope to engage in further collaborations with Geert-Jan and researchers in his group. Prof van Houtum also delivered a seminar to the Centre entitled A Predictive Maintenance Concept for Multi-Component Systems and, before he returned to Eindhoven, visited the Roy Hill Remote Operations Centre.
THEME 2 #
Theme 2 focuses on developing appropriate statistical and mathematical methods to provide tools for failure detection and prediction. The technical focus has been to provide alternative frameworks to analyse time-series data, especially degradation data. Theme 2 has been working with the Centre's researchers and industry partners on the projects below.
Research activities #
Degradation Modelling and Risk-Based Inspection Intervals: A Practical Approach, Gabriel Gonzalez #
Gabriel's PhD research focuses on advanced statistical methods for degradation modelling. In particular, he has been investigating Bayesian methods for estimating the remaining useful life of assets such as pipes. Efficient estimation, along with reliable uncertainty estimates, will allow him to develop a methodology for obtaining inspection intervals that will allow the maintainer to balance the risk of failure with the cost of inspection. Inspection intervals obtained in this way can be deployed as maintenance policies that will:
- Reduce the total cost of ownership of assets;
- Reduce the exposure of personnel to hazardous environments; and
- Simplify maintenance operations by reducing the workload on planners and schedulers.
He presented his work at the 2021 International Conference on Maintenance and Intelligent Asset Management.
Decision Support for Prognostics of Complex Systems: A Practical Approach Using Bayesian Networks, Ryan Leadbetter #
Ryan's PhD research aims to provide a decision support system for prognostic asset health management. The use of a decision support system will allow engineers to:
-
quickly assess the current and forecasted health of an asset given the available evidence and the planned operation;
-
hypothesise which components are most likely to be contributing to poor overall asset health; and
-
model the effects of different modes of operation on the likelihood of asset failure.
This information will assist planners with critical maintenance decision making through a data-driven approach to replacement policies on valuable assets
During one of his placements related to his research, Ryan developed a Bayesian method for combining expert information with heavily censored data to obtain more sensible and reliable estimates of component lifetimes. He presented his work at the 2021 International Conference on Maintenance and Intelligent Asset Management. The accompanying conference paper, " Informative Bayesian Survival Analysis to Handle Heavy Censoring in Lifetime Data " was published in a special edition of IEEE Xplore.
Modelling Lifetime Dependence of Heterogeneous Components via Sequential Order Statistics, Tim Pesch #
Tim is applying sequential order statistics (SOS) to multi-component, load-sharing systems in order to model their lifetime. Generators that together produce a specific power output or multiple wash tanks which filter a polluted substance are examples of such systems. SOS generalises an ordinary order statistic that allows modelling a dependence structure between components. The main idea is that upon the failure of one component, the lifetimes of the remaining components can change. The model further considers either all components to be heterogeneous or heterogeneous groups of homogeneous components. This assumption is feasible if not all generators are of the same type or if wash tanks operate in series, for instance. Tim's two main results of his first year at the CTMTDS prove that powerful tools can be used to better understand component and system behaviour. The results have been gathered in a paper draft and the research team will submit it to 'Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry' in the near future.
Reservoir Time-Series Analysis: Foundations and Applications, Braden Thorne #
Braden Thorne 's research will improve concept drift detection algorithms using reservoir computing. Such algorithms can be useful to industry for fault detection and/ or predictive maintenance.
Reservoir computing is a framework for supervised machine learning tasks. The underlying idea is to take some time series and inject it into a high dimensional recurrent network to construct a representation of the data in what we call the reservoir space. Up to this point, his research has focused on ways of training this reservoir space to desired outputs or labels and has done so with impressive results across many tasks and data sets. However, the reservoir space in and of itself is rich with information that can inform us about the original data stream without the need for training. The ability to use the reservoir in such an unsupervised way opens the way to new potential tasks, particularly ones where we don't have labels or targets to train.
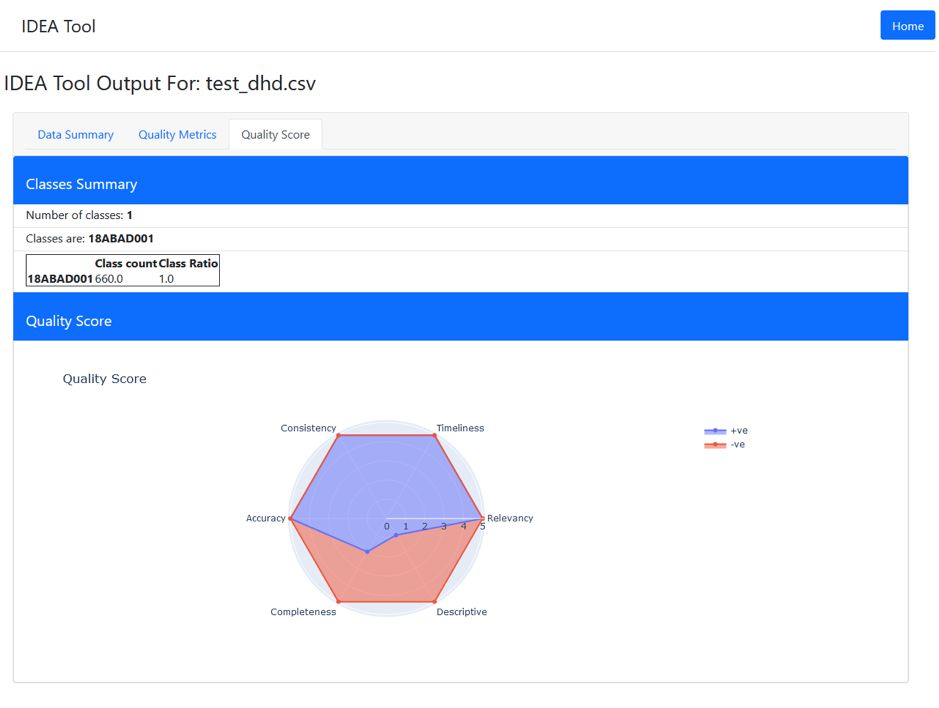
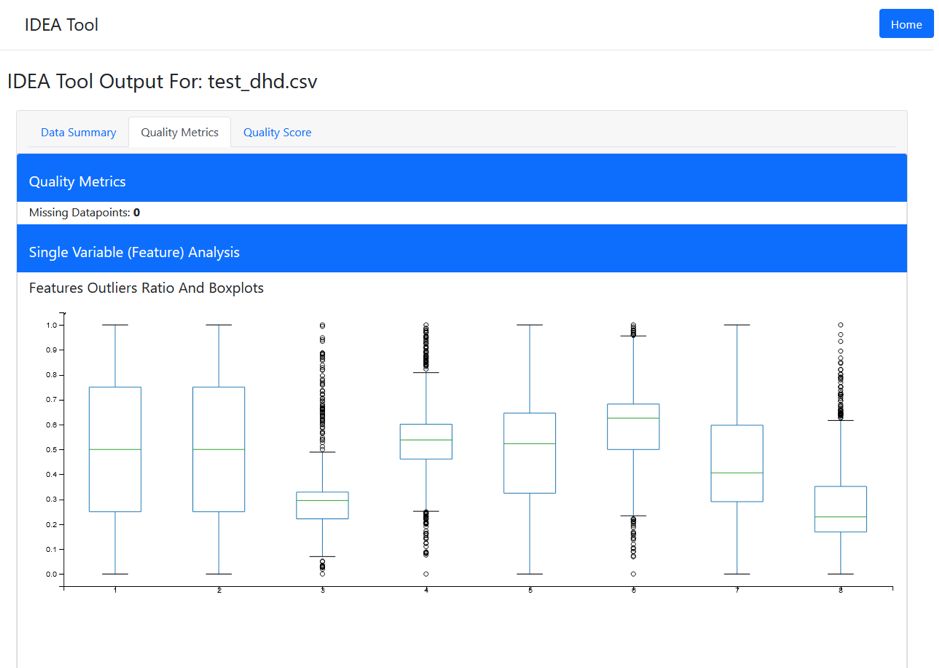
IDEA Tool - Assessing the Suitability of a Data Set #
TheIDEA (Integrated Data Evaluation and Annotation) toolcame out of early work in the Centre where researchers wanted to assess whether data sets would be suitable for classification or prediction. This tool assesses if there is sufficient structure or information so an analyst does not waste time wrangling and cleaning data before using it for prediction or classification. The IDEA tool being developed by the Centre has additional features beyond existing web-based tools, and researchers are currently working with software developers at CSIRO to develop an implementation that can be tested by the Centre's industry partners.
Data-driven labelling for process plant event data #
Plant operators can sometimes find it difficult to accurately label events such as failures, particularly on complex pieces of equipment such as those in alumina refineries. Working closely with Alcoa data scientists, Centre researchers developed advanced clustering techniques to consistently identify and cluster unlabelled events. This collaborative work was published in an open access paper and a LinkedIn post summarising the work attracted 80K views.
FASCINATE - Failure And Systematic Cascade Identification with Network Analysis of Temporal Events #
FASCINATE uses maintenance work order records to analyse co-occurrence of unscheduled maintenance events and then predict potential causal failure links. Further analysis with network tools then unveils potential cascading failure, bottle necks and "super-spreaders" in the plant. This collaborative work was published in an open access paper (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9524642).
PLACE - Pseudo-Linear Approximation to Chaotic Evolution for Nonlinear Time Series Analysis #
PLACE is a nonlinear time series modelling package distributed via GitHub and implemented in Julia for modelling of chaotic dynamics with radial basis functions and description length. The algorithms underlying the code have resulted in multiple publications over many years. The current (Julia) implementation is new and takes advantage of multiple processor architectures for modelling of industrial data in the resource industry.
Research Presentations #
At the recent May Researchers Catch-Up, Theme 2 PhD candidates Ryan Leadbetter and Braden Thorne presented their industry placement research projects to an industry/academic audience. Ryan's talk was entitled An alternative approach to conventional methods of belt wear modelling and forecasting, and Braden presented his work on A computer vision based approach to measuring remaining useful life of sizer barrels.
Stay tuned for our next issue in June where we will cover: #
- Research Theme 1 - Research Focus
- New publications
- Research updates