This month's newsletter focuses on Research Theme 1 - Support the maintainer.
IN THE SPOTLIGHT #
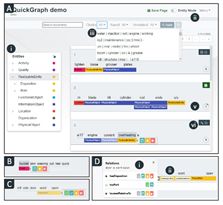
Congratulations to Tyler Bikaun whose paper "QuickGraph: A Rapid Annotation Tool for Knowledge Graph Extraction from Technical Text" was accepted into the Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, a top-ranking NLP conference.
Team News #
We are pleased to announce that Chau Nguyen's PhD research proposal titled Query Embedding for Multi-hop Reasoning over Technical Domains has been accepted by the Board of the Graduate Research School at UWA.
We are also pleased that Débora Corrêa is now a Chief Investigator for the Centre. Débora worked as a Research Fellow in Themes 1 and 2 from 2019 to 2021. This year Débora commenced an appointment at the UWA Computer Science Department and will continue supervising and mentoring students in the Centre.
Theme 1 - Support The Maintainer #
Theme 1 Activities #
Theme 1 is dedicated to developing techniques for extracting valuable knowledge from the textual and structured components of maintenance work orders and failure mode effects analysis (FMEA) data. The research will enable a move to machine readable text, improving work management and reliability engineering productivity and unlocking valuable information, particularly for calculating reliability metrics and determining failure modes.
Theme 1 PhD research #
Technical Language Processing for Industrial Maintenance Records, Tyler Bikaun #
Tyler's PhD research explores how the technical language found in industrial maintenance records differs from standard English corpora. Technical language processing remains understudied, with best practice frameworks and benchmarks for data sets and tasks not well established and understood. Tyler plans to use his research to structure information found in maintenance records and improve his understanding of the performance of assets and the optimisation of maintenance strategies.
Structuring the information within these fields could further enable Industry 4.0 .
Tyler's project will be split into three phases:
- Investigation of annotator behaviour under technical sequence labelling tasks,
- Development of an active learning framework for entity typing, and
- Investigation of the practical applications of active learning for entity typing within industrial maintenance.
A pattern-based natural language interface for knowledge graph querying, Ziyu Zhao #
Ziyu's PhD research focuses on how to structure a query of a knowledge graph so maintenance personnel and reliability engineers can ask questions to find information in the same way we use Google search.
Knowledge graphs encapsulate a wealth of valuable maintenance knowledge, such as historical asset information and failure modes associated with specific assets. Currently, we must formulate a query via a formal query language like Cypher to ask questions about a knowledge graph. However, reliability engineers have little to no knowledge of formal languages, preventing them from being able to query knowledge graphs directly. To bridge this gap, Ziyu is developing a pattern-based natural language interface enabling reliability engineers to ask key questions of a knowledge graph directly.
Ziyu presented her research to the Centre at the February Researchers Catch-up .
Reasoning about technical language for incomplete knowledge graphs using query embedding, Chau Nguyen #
Chau's PhD research focuses on the challenge of finding information from knowledge graphs when there is incomplete data or unconventional language such as jargon.
Reasoning about the text in maintenance work orders is an open challenge since they commonly contain " out-of-vocabulary" words. We refer to these types of text as "unstructured", as the text includes many abbreviations and jargon, preventing a language tool from understanding their meaning. Chau plans to overcome this challenge by 'query embedding for Knowledge Graphs (KGs)' using a multi-hop reasoning method. He will also try and solve the problem of incomplete knowledge graphs, an issue common when using data in real situations. Insufficient data is a critical issue because a query language cannot be used to reason about technical texts if knowledge graphs are incomplete.
Chau presented research to the Centre at the March Researchers Catch-up.
Theme 1 Tools and Projects #
Redcoat - Collaborative annotation for short text #
Michael Stewart developed Redcoat to allow users to establish training datasets to train state-of-the-art machine learning models to understand technical language.
Redcoat is the foundation for many Theme 1 projects. Theme 1 researchers regularly meet to collaboratively annotate thousands of maintenance work orders, and they have been joined by BHP SMEs to help annotate using their expert knowledge.
QuickGraph - Rapid knowledge graph construction from text #
Tyler Bikaun developed QuickGraph as an alternative to Redcoat. QuickGraph allows users to create annotated datasets for the construction of knowledge graphs. It features a comprehensive annotation interface, automatically creates a knowledge graph from the annotated texts, and contains features for reducing annotation effort and improving consistency.
Future work of Theme 1 involves using QuickGraph to capture causal information within notification data.
Tyler demonstrated QuickGraph in May at the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
LexiClean - Rapid multi-task lexical normalisation #
LexiClean is a tool designed by Tyler Bikaun for rapid multi-task annotation of noisy corpora for the task of lexical normalisation.
User-generated texts such as maintenance work orders and notifications can contain significant noise. This noise can reduce the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms such as those used in information extraction tasks like named entity recognition.
Tyler demonstrated LexiClean in November at the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing .
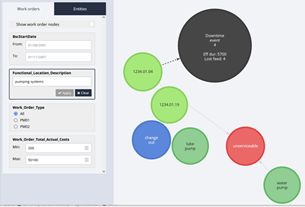
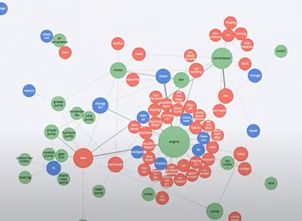
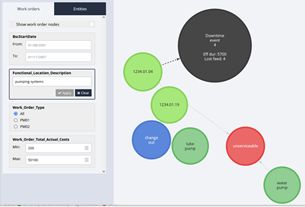
Echidna - Knowledge graph for maintenance data #
Michael Stewart developed Echidna to use a knowledge graph to visualise entities for unstructured text and maintenance work orders. It also looks at other maintenance work-related fields and links to the delay accounting system. Echidna allow reliability engineers to see what failure modes cause delays.
In February, Michael presented an overview of Echidna to a team of Grundfos ’ senior reliability engineers at the Grundfos Ideation Workshop.
Failure mode classification from MWO texts using Echidna #
One of the key features in Echidna is the ability to automatically classify failure modes ("leak", "broken" etc) into their corresponding failure mode category using machine learning.
This allows reliability engineers to group similar failure modes together and gain an understanding of the prevalence of particular failure modes in their data, and the relationships between those failure modes and particular asset types.
Linking fields in delay accounting and CMMS data sets by functional location using Echidna #
Echidna also allows for the incorporation of Delay Accounting data into the visualisation.
This enables the end user to easily see the downtime events associated with particular assets and obtain rapid insights into their datasets in a way that was not previously possible.
Platypus - fast, reproducible, reliability measure estimation #
Platypus, developed by Tyler Bikaun, is a collaborative tool for adaptive reliability measure estimation and knowledge elicitation built using modern web-development frameworks. This tool augments the traditional workflow of reliability engineers when determining reliability measures (such as MTBF/MTTF) by employing technical language processing.
Periscope #
Periscope is a software tool developed by Research Theme 1 and Translation Theme 5 in collaboration with BHP Nickel West. The tool aims to centralise and semi-automate the reliability estimation process using natural language processing and expert-in-the-loop techniques.
The tool builds on the functionality of Platypus by identifying and using end-of-life event information contained within semi-structured data captured in maintenance management systems.
Tyler presented this tool to the Centre at the Researchers Catch-up in June.
KOALA Project #
The KOALA project (KnOwledge GrAph Leveraging Asset relationships) aims to bring together multiple knowledge organisation systems into a single knowledge graph that facilitates natural language queries on maintenance data.
Ziyu and Chao have been working on reviewing the substantial number of taxonomies, data models, and ontologies available in the maintenance domain to answer the following:
- What knowledge organisation systems are available for industrial manufacturing equipment?
- What criteria would we use to assess their suitability to enrich maintenance-related data from unstructured texts stored in a knowledge graph?
Quantifying lubrication costs #
Michael Stewart has developed code to apply technical language processing techniques to maintenance work order texts to automatically calculate the cost of lubrication-related failures.
Lubrication is a crucial element in any rotating equipment's efficiency and life expectancy. This research allows us to quantify lubrication cost issues as a percentage of total maintenance cost and identify where the main 'bad actors' are so they can be addressed.
In May, Michael Stewart, Tyler Bikaun and Melinda Hodkiewicz joined Taku Mtabeni to present a live Cost of Lubrication Power BI dashboard to BHP reliability engineers and managers.
Theme 1 Training and Workshops #
Data Science in Reliability Training #
CORE Skills have developed a Data Science in Reliability Course in collaboration with Melinda Hodkiewicz and Tyler Bikaun.
The course is designed to give reliability engineers, data analysts, or other technical staff a toolkit to develop scalable maintenance record processing and extraction for key reliability figures like MTBF. Staff from some of our industry partners will attend the first offering of this course in July.
Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence #
Theme 1 researchers will present their research at the 35th Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AIAI2022) in Perth, Western Australia, in December 2022.
AI2022 is an annual event to advance AI communication between academic researchers and industry in Australia. Chief Investigators for Research Theme 1, [Associate Professor Wei Liu](http://Associate Professor Wei Liu ) , Dr Tim French and Dr Débora Corrêa are on the committee. Prof Melinda Hodkiewicz and Prof Mark Reynolds are on the Advisory Board.
We look forward to providing you with more information on the Centre's contribution in December.
It is exciting to see the research of Theme 1 and Caitlin Woods , a System Health Lab Research Group member, being adopted and made into demos by [Oxford Semantic Technologies](http://Oxford Semantic Technologies) to help improve maintenance strategies. Check out the blog post that Caitlin co-wrote with Oxford Semantic Technologies entitled Transform Disparate Engineering Data into Structured Knowledge.
Stay tuned for our next issue in July where we will cover: #
- Translation Theme 5 - Research Focus
- New publications
- Research updates